Enamel Basics
Did you know that enamel is the strongest tissue in the human body? It’s the only human tissue that can survive a fire due to the fact that it’s highly mineralized, making it harder than both dentin and bone. Enamel is known for the vascular and cellular structure meaning it has no cells or blood vessels, because of that it cannot regenerate itself if it gets damaged. Enamel is also dynamic, meaning it goes through stages of demineralization and remineralization by exchanging ions with the surrounding environment.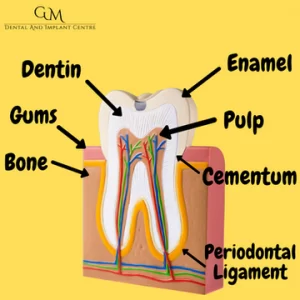
Besides being the hardest tissue in the body, the enamel is also semipermeable, allowing small molecules and ions to pass through the innermost enamel is more permeable than the outermost enamel.
Enamel has no collagen making it inflexible and brittle. High mineralization not only accounts for the hardness of enamel but also for its translucency, so the colour of the tooth is affected by the colour of the underlying dentin, it has low thermal conductivity and expansion, so it pickups the pulse from any temperature fluctuations.
What is Enamel made off?
Enamel is made up of three parts, the inorganic part is made up of mineral witch form 95 to 97% of the structure, while the organic material is less than 1%, the remaining 2 to 3% is made up with water.
Enamel is not perfect, if we look closely under the microscope you may clearly some lamellae, tufts and even spindles. What are these lamellae, tufts and spindles exactly?
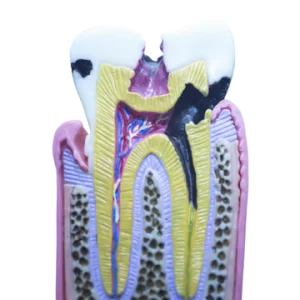
Enamel Lamellae is a crack extending towards dentin enamel junction, containing abnormally high levels of organic material, this defect provides a pathway of entry for bacteria that may initiate caries first weakening the tooth. Enamel tufts, on the other hand, are formed due to a change in the orientation of the rods, they appear as branched dark short lines and exhibit high levels of proteins stop expand from resenting in enamel junction into about 1/10 of the enamel thickness. Lastly, enamel spindles represent the trapped don’t applause processes that felt to withdraw during the enamel mineralization, they appear short dark finger-like extensions from dentin enamel junctions into the enamel.
Does ageing affect your enamel?
Yes, as you age your enamel will age too, first all the enamel becomes less permeable due to a reduction in the spaces between the crystals, your teeth may become more sensitive to the attrition and wear. On the bright side, your enamel becomes harder with age as the hydroxyapatite crystals become more mineralized, however as the enamel becomes thinner the underlying dentin colour will become more visible causing the teeth to darken, last but not least, the risk of caries actually decreases with age, due to certain ion exchanges between the tooth and the oral environment.
“I have just had my dental implants fitted the whole procedure went really smooth,...”
“I had my dead tooth broken so implant was the only option to make...”
“I’ve been struggling with my teeth for many years and I’ve lost hope that...”
“My daughter attended this practice in 2010 and finished her treatment in 2013. The...”
“I was treated here years ago as a teenager and so did a few...”
“My daughter had her orthodontic treatment here over a 3 year period. Dr Coonar...”
